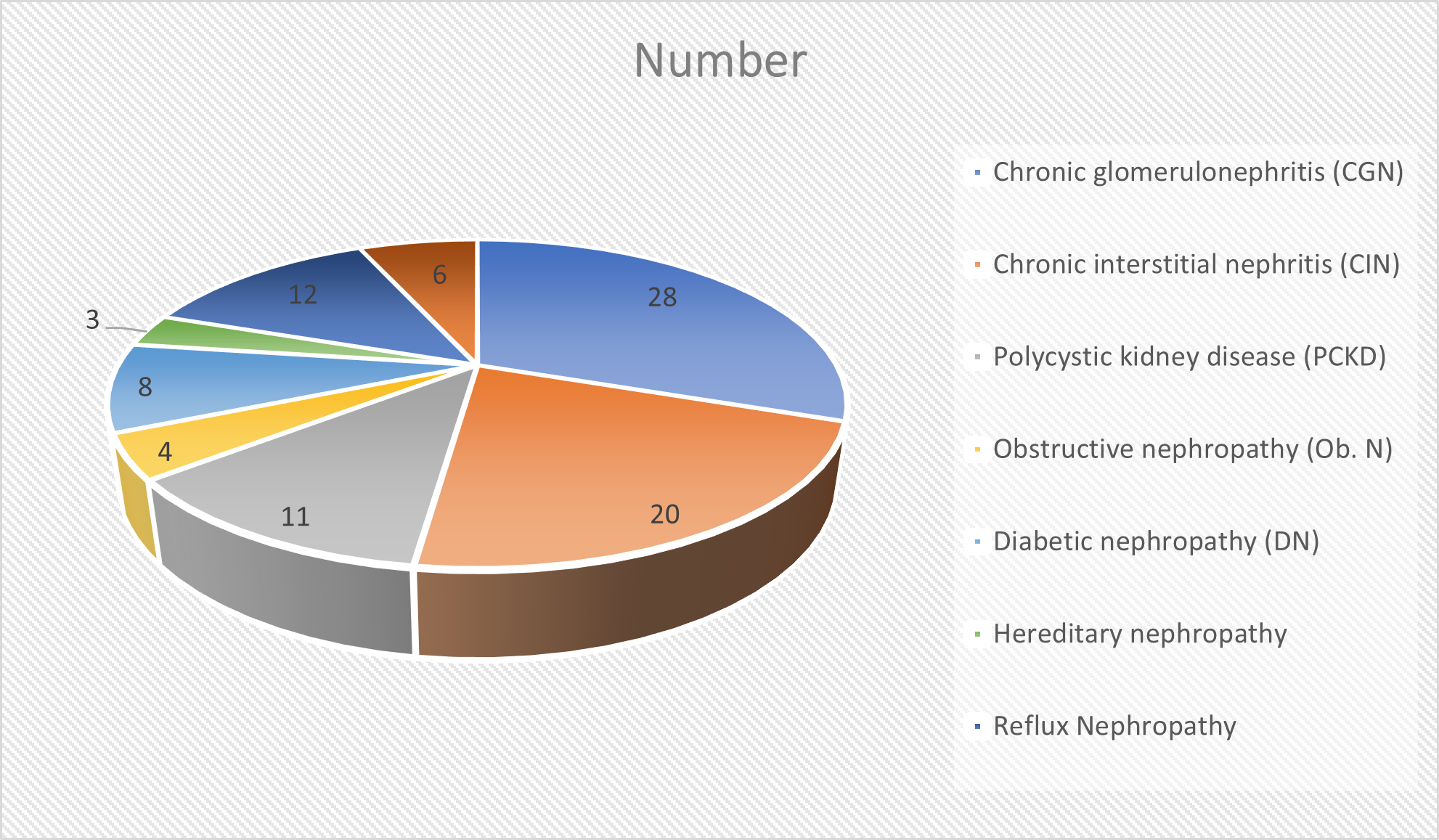
Aim: To evaluate anesthetic management in renal transplant patients. Methodology: Ninety- two renal transplant patients were part of the study. Parameters such as type of transplant, reason for chronic kidney disease, preoperative data, history of dialysis, preoperative anesthesia management, monitoring details and the outcome were recorded. Results: Chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) in 28 (30.4%), chronic interstitial nephritis (CIN) in 20 (21.7%), polycystic kidney disease (PCKD) in 11 (11.9%), obstructive nephropathy (Ob. N) in 4 (4.3%), diabetic nephropathy (DN) in 8 (8.7%), hereditary nephropathy in 3 (3.2%), reflux nephropathy in 12 (13%) and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) in 6 (6.5%). In 32 (35.6%) patients, isoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 25.1 minute, in 40 (43.4%), desflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 22.7 minutes and in 20 (21.7%), sevoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 32.1 minutes. A significant difference was observed (P< 0.05). Conclusion: Anesthesia management has made renal transplantation safe and predictable. Postoperative maintenance of renal transplant patients have contributed to the success of renal transplant programme.
The number of solid organ transplants performed worldwide is ever increasing. The improved survival rates are the result of well-established surgical techniques and effective immunosuppressive therapy [1]. All this has led to an increase in number of patients who present for either elective or emergency non-transplant surgery [2]. Laparotomy for small bowel obstruction, hip arthroplasty given the increased risk of fracture and avascular necrosis as a result of chronic steroid use causing bone demineralization and osteoporosis, lymph node excision and biopsy because of increased risk of lymphoproliferative disease, native nephrectomy in kidney transplant recipients, bronchoscopy in lung recipients, biliary tract interventions in liver recipients, and abscess drainage because of increased risk of infection are just a few of the increased surgical needs in this population [3].
Vigilant intraoperative monitoring, optimization of intravascular fluid volume status to maintain maximum kidney perfusion, to avoid fluid overload, and early correction of electrolyte abnormalities are the crux of short and long term success of renal transplants [4]. With the expanding criteria for taking patients for kidney transplantation, anesthesiologists are likely to be encountered with more problems of the interaction of other co-morbid diseases and multiple drug therapies in the near future. Recipients involving cadaveric donor organs are often scheduled as urgent or emergency procedures [5]. However, a well-preserved kidney provides enough time to prepare the recipient and if necessary dialyze to normalize electrolyte and volume imbalance. Successful use of regional anaesthesia has been reported by some centers. Certain factors to be considered for the use of regional anaesthesia are uraemic bleeding tendency, effect of residual heparin given during dialysis, altered platelet function, decrease in coagulation factors and the duration of surgery [6]. Considering this, we attempted present study to evaluate anesthetic management in renal transplant patients.
Patients’ case record files were retrieved from the department. Parameters such as type of transplant, reason for chronic kidney disease, preoperative data, history of dialysis, preoperative anesthesia management, monitoring details and the outcome were recorded. Results of the present study after recording all relevant data were subjected for statistical inferences using chi- square test. The level of significance was significant if p value is below 0.05 and highly significant if it is less than 0.01.
Common reasons for end stage kidney disease was chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) in 28 (30.4%), chronic interstitial nephritis (CIN) in 20 (21.7%), polycystic kidney disease (PCKD) in 11 (11.9%), obstructive nephropathy (Ob. N) in 4 (4.3%), diabetic nephropathy (DN) in 8 (8.7%), hereditary nephropathy in 3 (3.2%), reflux nephropathy in 12 (13%) and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) in 6 (6.5%). A significant difference was observed \((P< 0.05)\) (Table 1, Figure 1).
| Variables |
Parameters |
Number |
P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reason for injury |
RTA |
62 |
Significant <0.05 |
| Fall |
40 |
||
| Domestic violence |
10 |
||
| Associated fracture |
Trans-scaphoid fracture |
23 |
Significant <0.05 |
| Radial styloid fractures |
14 |
||
| Mayo wrist score |
Excellent to good |
70 |
Significant <0.05 |
| Fair to poor |
42 |
||
| Lyon wrist score |
Excellent to good |
64 |
Significant <0.05 |
| Fair to poor |
48 |
||
| Wrist flexion/extension arc |
49.1 degree |
– |
|
| Wrist radial/ulnar deviation arc |
18.2 degree |
– |
|
| Wrist radial ulnar movement arc |
50.4 degree |
– |
|
| Forearm supination/pronation arc |
82 degree |
– |
|
| Grip strength |
68.2% |
– |
|
It was found in 32 (35.6%) patients, isoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 25.1 minute, in 40 (43.4%), desflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 22.7 minutes and in 20 (21.7%), sevoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 32.1 minutes. A significant difference was observed (P< 0.05) (Table 2).
| Inhalational agents | Number (%) | Recovery time (in mins) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isoflurane | 32 (35.6%) | 25.1 | 0.05 |
| Desflurane | 40 (43.4%) | 22.7 | |
| Sevoflurane | 20 (21.7%) | 32.1 |
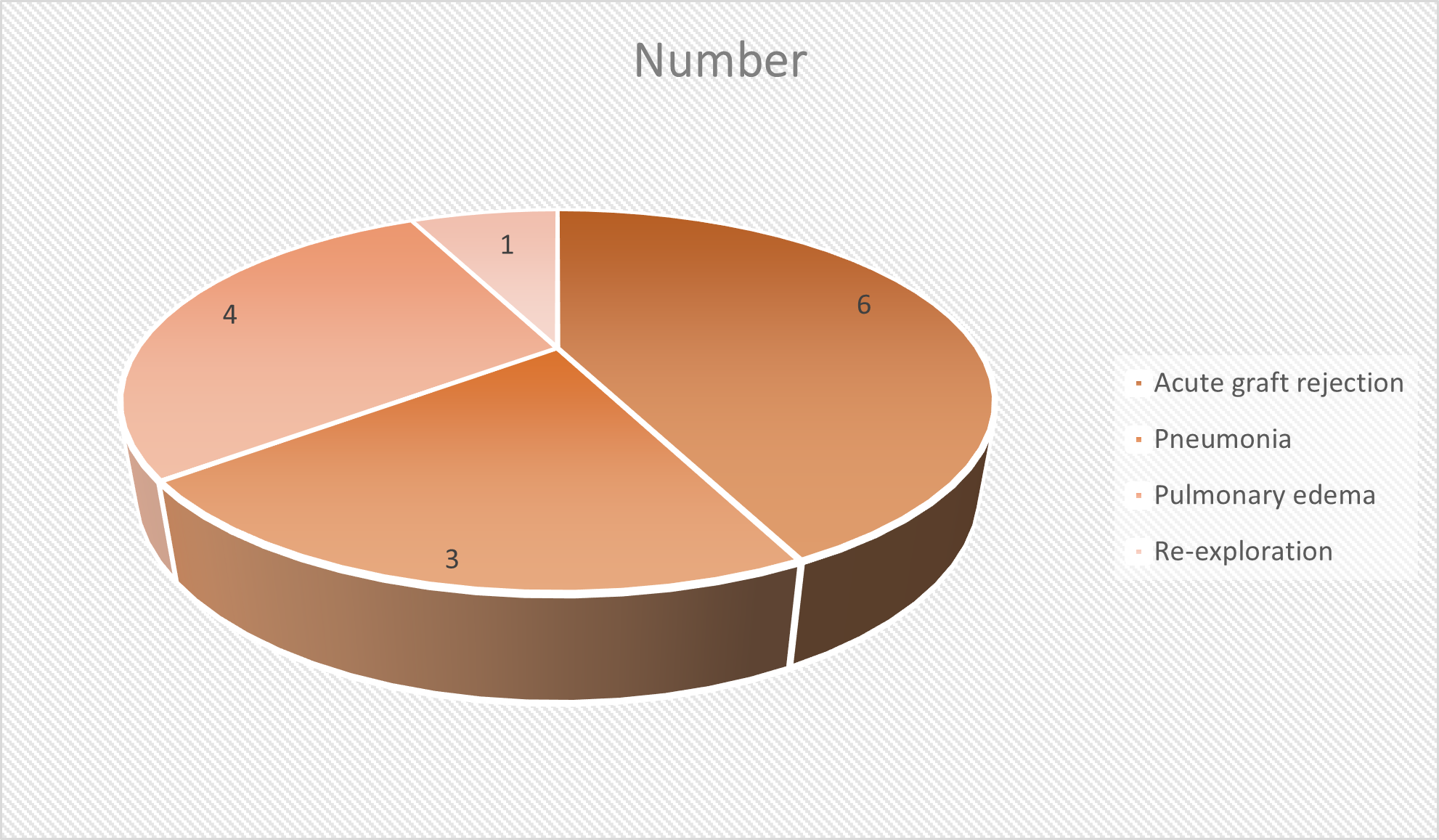
Post- operative complications were acute graft rejection in 6 (6.5%), pneumonia in 3 (3.2%), pulmonary edema in 4 (4.3%) and re-exploration in 1 (1%). A significant difference was observed \((P< 0.05)\) (Table 3, Figure 2).
| Complications | Number (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| Acute graft rejection | 6 (6.5%) | 0.05 |
| Pneumonia | 3 (3.2%) | |
| Pulmonary edema | 4 (4.3%) | |
| Re-exploration | 1 (1%) |
Our results found that chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) in 28 (30.4%), chronic interstitial nephritis (CIN) in 20 (21.7%), reflux nephropathy in 12 (13%), polycystic kidney disease (PCKD) in 11 (11.9%), diabetic nephropathy (DN) in 8 (8.7%), membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) in 6 (6.5%), obstructive nephropathy (Ob. N) in 4 (4.3%) and hereditary nephropathy in 3 (3.2%) were common reasons for end stage kidney disease. Tiwari et al., [9] included 100 patients with end stage renal disease and found that 92% were living and 8% were cadaveric related transplant. 92% were done electively. Most common co-morbidity recorded was hypertension in 49% patients. Predominant cause of end stage renal disease was chronic glomerulonephritis (41%). General anesthesia was technique of choice in all patients, 27 also received epidural. Invasive blood pressure monitoring was done in 3 patients with cardiac co-morbidities. 15% patients required blood transfusion. CVP maintained > 12 mmHg and maximum at de-clamping. Mean arterial pressure maintained above 95 mmHg. Ionotropic support required in 2 patients. 76% patients were transfused with only crystalloid (NS and/or RL) while 24 patients received a combination of both crystalloid and colloid. 97% patients were extubated postoperatively while 3% required ventilator support. Recovery time with desflurane was significantly less as compared to other inhalational agents. One patient died postoperatively.
It was observed that in 32 (35.6%) patients, isoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 25.1 minute, in 40 (43.4%), desflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 22.7 minutes and in 20 (21.7%), sevoflurane was inhalational agent and recovery time was 32.1 minutes. Hadimioglu et al., [10], the authors found that lactated ringer’s used in the perioperative period of renal transplant surgeries, resulted in similar potassium levels during the postoperative period, higher bicarbonate and pH levels, and also lower chlorides, despite using the similar infusion volume in comparison to normal saline solutions.
Low serum albumin levels leads to an increase in free fraction of the drug in plasma while uremia associated altered blood brain barrier can increase the levels of unbound drug crossing the blood brain barrier into CNS receptors. Hence, the dose of induction agents may need to be adjusted according to the volume status, acidic pH and increased sensitivity of the nervous system to these drugs. In chronic renal failure patients, the underlying rate and extent of thiopental distribution and elimination are much the same as in normal patients [11]. However, a higher dose of propofol is required to reach the clinical end point of hypnosis and bispectral index of 50. The hyperdynamic circulation and high plasma volume resulting from anemia can counteract the effect of low serum albumin explaining the higher dose requirement with propofol. Ketamine pharmacokinetics are not significantly changed by renal disease, but the hypertensive effects make it undesirable in patients with underlying hypertension. Etomidate is well tolerated and preserves hemodynamic stability [12].
